Description
This plugin allows you to manage and load site specific functions, scripts and CSS files into your WordPress site without the need to edit your theme’s functions.php or any other source file.
Settings and options include:
- Choose the type of customization you want to load; functions, scripts, CSS in any combination.
- Choose where you want the customizations to load; in the WordPress front-end, in the WordPress admin screens or both.
- Choose where you want to store your customization files, without the need to add to or modify your theme’s or your plugin’s source files.
Filter Support And Usage
WP Customizer supports multiple filters; the plugin’s filters allow you to
- modify the set of functions files that are about to be loaded
- modify the set of script files that are about to be loaded
- modify the characteristics of each script file that is about to be loaded and which will be passed as arguments to
wp_enqueue_script - modify the set of CSS files that are about to be loaded
- modify the characteristics of each CSS file that is about to be loaded and which will be passed as arguments to
wp_enqueue_style
Each filter will be only be called if the customization type is enabled in the plugin’s options; if a customization type is enabled but no files are found to be loaded, the filter will still be called but will be passed an empty argument.
As with all WordPress filters, any filter hook function should either return the modified argument or the original argument if no modification were made.
wp_customizer_functions, wp_customizer_admin_functions, wp_customizer_common_functions
The functions filters are called when preparing to load the list of front-end functions (wp_customizer_functions), of admin functions (wp_customizer_admin_functions) and of common functions (wp_customizer_common_functions). The arguments that each filter hook function receives is identical in all cases. The filter hook function takes a single argument which is an array of file names.
Example: Prevent all function files from loading by returning an empty file list.
add_filter('wp_customizer_functions', 'function_handler', 10, 1);
function function_handler($files) {
// $files = array(
// array(
// 'file' => (absolute path of function file)
// ),
// array(...)
// );
return array();
}
wp_customizer_scripts, wp_customizer_admin_scripts, wp_customizer_common_scripts
The scripts filters are called when preparing to load the list of front-end scripts (wp_customizer_scripts), of admin scripts (wp_customizer_admin_scripts) and of common scripts (wp_customizer_common_scripts). The arguments that each filter hook function receives is identical in all cases. The filter hook function takes a single argument which is an array of file details.
Example: Add jQuery as a dependency to all scripts and enable each script to load in the post’s footer.
add_filter('wp_customizer_scripts', 'script_handler', 10, 1);
function script_handler($files) {
// $files = array(
// array(
// 'file' => (absolute path of script file),
// 'handle' => (auto-generated handle for script),
// 'src' => (URL of script file),
// 'deps' => (dependencies, defaults to an empty array),
// 'ver' => (version, defaults to false),
// 'in_footer' => (load in footer, defaults to false),
// ),
// array(...)
// );
foreach ($files as $file) {
$file['deps'] = array('jquery');
$file['in_footer'] = true;
}
return $files;
}
wp_customizer_css, wp_customizer_admin_css, wp_customizer_common_css
The CSS filters are called when preparing to load the list of front-end CSS (wp_customizer_css), of admin CSS (wp_customizer_admin_css) and of common CSS (wp_customizer_common_css). The arguments that each filter hook function receives is identical in all cases. The filter hook function takes a single argument which is an array of file details.
Example: Override the media type for all CSS files to use the screen media type.
add_filter('wp_customizer_css', 'css_handler', 10, 1);
function css_handler($files) {
// $files = array(
// array(
// 'file' => (absolute path of css file),
// 'handle' => (auto-generated handle for CSS),
// 'src' => (URL of CSS file),
// 'deps' => (dependencies, defaults to an empty array),
// 'ver' => (version, defaults to false),
// 'media' => (media type, defaults to 'all')
// ),
// array(...)
// );
foreach ($files as $file) {
$file['media'] = 'screen';
}
return $files;
}
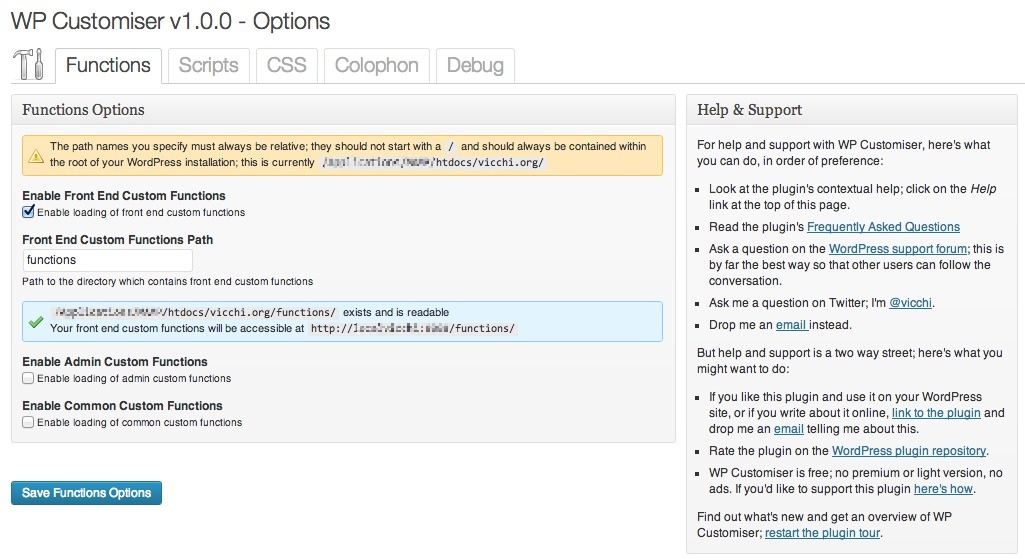
Screenshots
Installation
- You can install WP Customizer automatically from the WordPress admin panel. From the Dashboard, navigate to the Plugins / Add New page and search for “WP Customizer” and click on the “Install Now” link.
- Or you can install WP Customizer manually. Download the plugin Zip archive and uncompress it. Copy or upload the
wp-customizerfolder to thewp-content/pluginsfolder on your web server. - Activate the plugin. From the Dashboard, navigate to Plugins and click on the “Activate” link under the entry for WP Customiser.
- Prepare your customization files. By default, WP Customizer looks for front-end functions in a directory named
functions, for front-end scripts in a directory namedscriptsand for front-end CSS files in a directory namedcss. - Admin screen customizations are placed in a similar set of directories, prefixed with
admin_, as inadmin_functions,admin_scriptsandadmin_css. - Customizations common to both the front-end and the admin screens are placed in directories prefixed with
common_, as incommon_functions,common_scriptsandcommon_css. - You can either create the default directories and place your customization files in them or create your own directory hierarchy.
- Now you can configure the loading of each type of supported customization. From the Dashboard navigate to Settings / WP Customizer and enable loading of the customization files as you require.
- If you choose to use a non-default set of directory name, you should ensure the plugin’s options are updated to reflect this.
FAQ
- Installation Instructions
-
- You can install WP Customizer automatically from the WordPress admin panel. From the Dashboard, navigate to the Plugins / Add New page and search for “WP Customizer” and click on the “Install Now” link.
- Or you can install WP Customizer manually. Download the plugin Zip archive and uncompress it. Copy or upload the
wp-customizerfolder to thewp-content/pluginsfolder on your web server. - Activate the plugin. From the Dashboard, navigate to Plugins and click on the “Activate” link under the entry for WP Customiser.
- Prepare your customization files. By default, WP Customizer looks for front-end functions in a directory named
functions, for front-end scripts in a directory namedscriptsand for front-end CSS files in a directory namedcss. - Admin screen customizations are placed in a similar set of directories, prefixed with
admin_, as inadmin_functions,admin_scriptsandadmin_css. - Customizations common to both the front-end and the admin screens are placed in directories prefixed with
common_, as incommon_functions,common_scriptsandcommon_css. - You can either create the default directories and place your customization files in them or create your own directory hierarchy.
- Now you can configure the loading of each type of supported customization. From the Dashboard navigate to Settings / WP Customizer and enable loading of the customization files as you require.
- If you choose to use a non-default set of directory name, you should ensure the plugin’s options are updated to reflect this.
- Why should I use this plugin?
-
A standard WordPress install is incredibly powerful and flexible. For a lot of people, WordPress out of the box plus one of the stock WordPress themes is enough. But the possibilities for customization are endless; you can add plugins and other themes. Sometimes these do just what you want. Sometimes you need to … tweak WordPress. A very high proportion of the customization advice you’ll find on the web starts with these lines … add the following to the end of your theme’s
functions.phpor even worse, advises that you modify the source code of your theme or your plugins. This is bad for many reasons:- Editing your theme’s
functions.phpmakes theme specific customizations; change your theme and your customizations will no longer get loaded. - When your theme and plugins get updated you’ll find all your careful hand crafted customizations get overwritten and lost.
- A lot of theme and plugin authors won’t offer support for changes you might have made to the source code.
- Your customizations might work; but you might also inadvertently make some other changes which will stop things working.
WordPress doesn’t yet support a way for site specific customizations to be made and loaded without touching theme, plugin or core files; that’s what this plugin is for. When WordPress does support such a way, this plugin will thankfully be obsolete.
- Editing your theme’s
- How do I get help or support for this plugin?
-
In short, very easily. But before you read any further, take a look at Asking For WordPress Plugin Help And Support Without Tears before firing off a question. In order of preference, you can ask a question on the WordPress support forum; this is by far the best way so that other users can follow the conversation. You can ask me a question on Twitter; I’m @vicchi. Or you can drop me an email instead. I can’t promise to answer your question but I do promise to answer and do my best to help.
- Is there a web site for this plugin?
-
Absolutely. Go to the WP Customizer home page for the latest information. There’s also the official WordPress plugin repository page and the source for the plugin is on GitHub as well.
- I’ve installed this plugin but it doesn’t do anything?
-
By default the plugin installs with no customizations loading; you’ll need to enable them as you need. See the Installation section for more details on how to do this.
- I don’t know PHP or JavaScript or jQuery or CSS; what customizations do I need?
-
To answer the first part of this question, it’s probably best to start at the beginning and get a solid grounding in these tools and technologies before you start making customizations.
To answer the second part of this question, if you don’t know what customizations you need then this plugin probably isn’t for you.
- I don’t want to load all of the functions, scripts or CSS files I have; can I select which ones get loaded?
-
WP Customizer looks in each of the directories that you’ve configured (or left as the default) for each type of customization to load. To stop a specific file loading, simply rename it so that the first character of the file name is the underscore (
_) character and that file will be skipped over when the plugin is looking for files to load. If other words, just renamefoo.phpto_foo.php. - I’m a WordPress power user and want to specify things like dependencies for my scripts or make my CSS customizations load in the page footer; can I do this?
-
Yes you can. Take a look at the Filter Support and Usage section for information on how to use the plugin’s filters to do all of this and more. In fact, by using the plugin’s filters you can specify every single option that the WordPress
wp_enqueue_scriptandwp_enqueue_styleAPI calls accept. - I’ve enabled functions/scripts/css and supplied a path but my function/script/css isn’t loading?
-
There’s a couple of things that might be happening here. Your file type might be incorrect; your path might not exist or be readable, your file might not exist or be readable or your file might be disabled (starting with an ‘_’). The plugin’s Debug tab is designed to help
diagnose this sort of thing. The Debug tab performs a dry run, without actually loading any files, and checks that files and directories exist and are readable. If you see any entries highlighted in yellow then this will indicate that a file is probably disabled. If you see any entries highlighted in red then this will indicate that a file or directory either doesn’t exist or is not able to be read. - WP Customizer has crashed my website/killed my cat/made it rain; what do I do?
-
This is unlikely but always possible. A customization file with errors in it can have unforeseen consequences. If this does happen firstly disable all your customization files by renaming them to have an underscore (
_) as the first character. Hopefully things will be OK again. Now rename each customization file back by removing the underscore, one by one, to narrow down which one breaks things. Now would also be a good time to defineWP_DEBUGin yourwp-config.phpfile to get some helpful error messages in your PHP log file.For the cases of expired felines or sudden precipitation, this is way outside what a WordPress plugin can do; it’s probably an unfortunate coincidence.
- What is all this talk of “customization”; I’m British and it’s spelt “customisation” … ?
-
I’m British too and yes, it’s spelt customisation over here, not customization. As both Oscar Wilde and George Bernard Shaw are quoted as saying ‘(Britain and America are) two nations, separated by a common language‘. By default, WP Customizer uses American English, but if you’re British and you want British English instead, simply define
WP_LANGto have a value ofen_GBin your site’swp-config.phpand WP Customizer will automagically become WP Customiser. - WP Customizer isn’t available in my language; can I submit a translation?
-
WordPress and this plugin use the gettext tools to support internationalisation. The source file containing each string that needs to be translated ships with the plugin in
wp-customizer/lang/src/wp-customizer.po. See the I18n for WordPress Developers page for more information or get in touch for help and hand-holding. - I want to amend/hack/augment this plugin; can I do this?
-
Totally; this plugin is licensed under the GNU General Public License v2 (GPLV2). See http://www.gnu.org/licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.txt for the full license terms.
Reviews
Contributors & Developers
“WP Customizer” is open source software. The following people have contributed to this plugin.
ContributorsTranslate “WP Customizer” into your language.
Interested in development?
Browse the code, check out the SVN repository, or subscribe to the development log by RSS.
Changelog
The current version is 1.0.1 (2013.09.18)
1.0.1
- Release 2013.09.18
- Fixed: Annoying Markdown syntax in plugin overview text.
- Fixed: Pointer help file is now included; this was missing in v1.0.0.
- Added: Pointer text for the Debug tab.
1.0.0
- Released 2013.05.29
- First version of WP Customizer released